Free, Damped and Forced Vibrations
Free, Damped and Forced Vibrations: Overview
In this topic, we will be able to know the difference between free, damped and forced vibrations with their definition. This topic also covers condition for producing different vibrations and the concept of resonance.
Important Questions on Free, Damped and Forced Vibrations
The frequency of first overtone of a closed organ pipe of length is A hole is made at a distance of from the closed end. Now the frequency of first overtone of open pipe is.
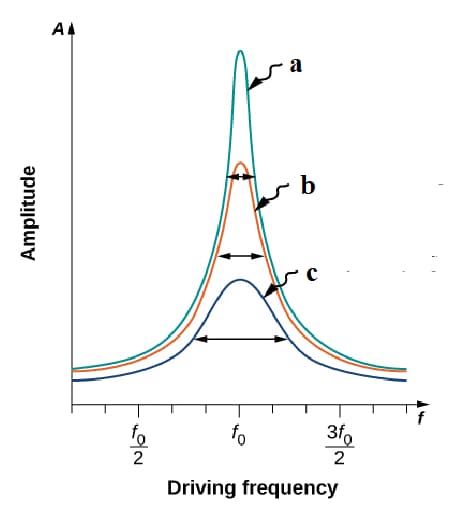
The graph of amplitude vs. driving frequency of a given oscillator is shown. Which one of the following sequence is correct based on their damping constant?
Point out the differences between the free oscillation and forced oscillation.
The forced oscillation does face the damping effect. But the supply of external force results in gaining the energy thereby maintaining constant amplitude.
When a body oscillates by being influenced by an external periodic force, it is called free oscillation and forced oscillation possesses constant period only without any external force to set the oscillation.
What are the differences between free and forced oscillations?
Frequency will not change in damped oscillation and will change in free oscillation.
Mention the differences between the damped oscillations and free oscillations.
The swinging pendulum in a laboratory is an example of free oscillation.
In free oscillation, the amplitude of the oscillating body reduces and eventually comes to its mean position.
What are the differences between free and damped oscillation.
In case of damped oscillation, the displacement increases with time.
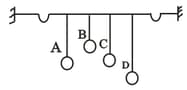
In the given arrangement which pair can represents the resonance.(All are simple pendulum).
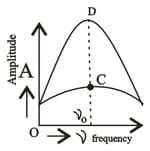
The variation of amplitude of forced oscillation vs driving frequency. Which part represents least damping.
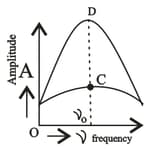
The variation of amplitude of forced oscillation vs driving frequency, which point represents the heavy damping.
A pendulum gradually stops oscillating as the body loses energy doing work against force of _____.(Friction/Gravitation)
Vibrations of constant amplitude are possible only in _____.(Medium/Vacuum)
The vibrations that can continue even after the external force is removed are called free vibrations or natural vibrations.
Natural frequency of a body depends on the shape, size, and _____ (elasticity/intensity) of the body.
In forced oscillation of a particle, the amplitude is maximum for a frequency of the force, while the energy is maximum for a frequency of the force, then
